İçindekiler
- 1. What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
- 2. Key Components of IoT
- 3. Applications of IoT in Smart Homes
- 4. IoT in Healthcare and Wearable Devices
- 5. Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Smart Manufacturing
- 6. IoT and Environmental Monitoring
- 7. IoT Security and Privacy Considerations
- 8. The Future of IoT: AI and Edge Computing
- 9. IoT Standards and Interoperability
- 10. Ethical and Social Implications of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that has been gaining increasing attention in recent years. It refers to the interconnection of everyday objects through the internet, allowing them to send and receive data. This network of connected devices has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work, with applications in areas such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing. As we continue exploring the Internet of Things (IoT), it’s important to understand the impact it can have on our daily lives and the opportunities it presents for innovation and efficiency.
One of the key aspects of exploring the Internet of Things (IoT) is understanding how it can benefit individuals and businesses. By connecting devices and systems, IoT can enable more efficient processes, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring. For example, in the healthcare industry, IoT devices can be used to track patients’ vital signs and provide early warnings of potential health issues. In manufacturing, IoT can streamline production processes and reduce downtime through predictive maintenance of equipment.
As we delve deeper into the world of IoT, it’s natural to have questions about its potential impact on privacy and security. With the proliferation of connected devices, concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity have become more prominent. It’s important to consider how to secure IoT devices and the data they generate, as well as how to ensure that personal information is protected.
One of the most intriguing aspects of exploring the Internet of Things (IoT) is the sheer scale of its potential. With billions of devices expected to be connected in the coming years, the possibilities for innovation are virtually limitless. From smart homes and cities to connected cars and wearable devices, IoT has the power to transform the way we interact with the world around us.
As we continue on this journey of exploring the Internet of Things (IoT), we will delve into the various applications of IoT in different industries, the challenges and opportunities it presents, and the future trends that are shaping this rapidly evolving field. Whether you’re a business looking to leverage IoT for increased efficiency, or an individual curious about the impact of IoT on your daily life, there is much to discover in the world of the Internet of Things. So, keep reading to uncover the exciting possibilities that IoT holds for the future.
1. What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects or “things” embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. These interconnected devices can range from simple household objects to complex industrial machines, and they can communicate and interact with each other to automate tasks and make data-driven decisions.
The concept of IoT has gained significant traction in recent years, as advancements in technology have made it more feasible to connect and control everyday objects through the internet. IoT has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare, agriculture, transportation, and manufacturing, by enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration of digital and physical systems.
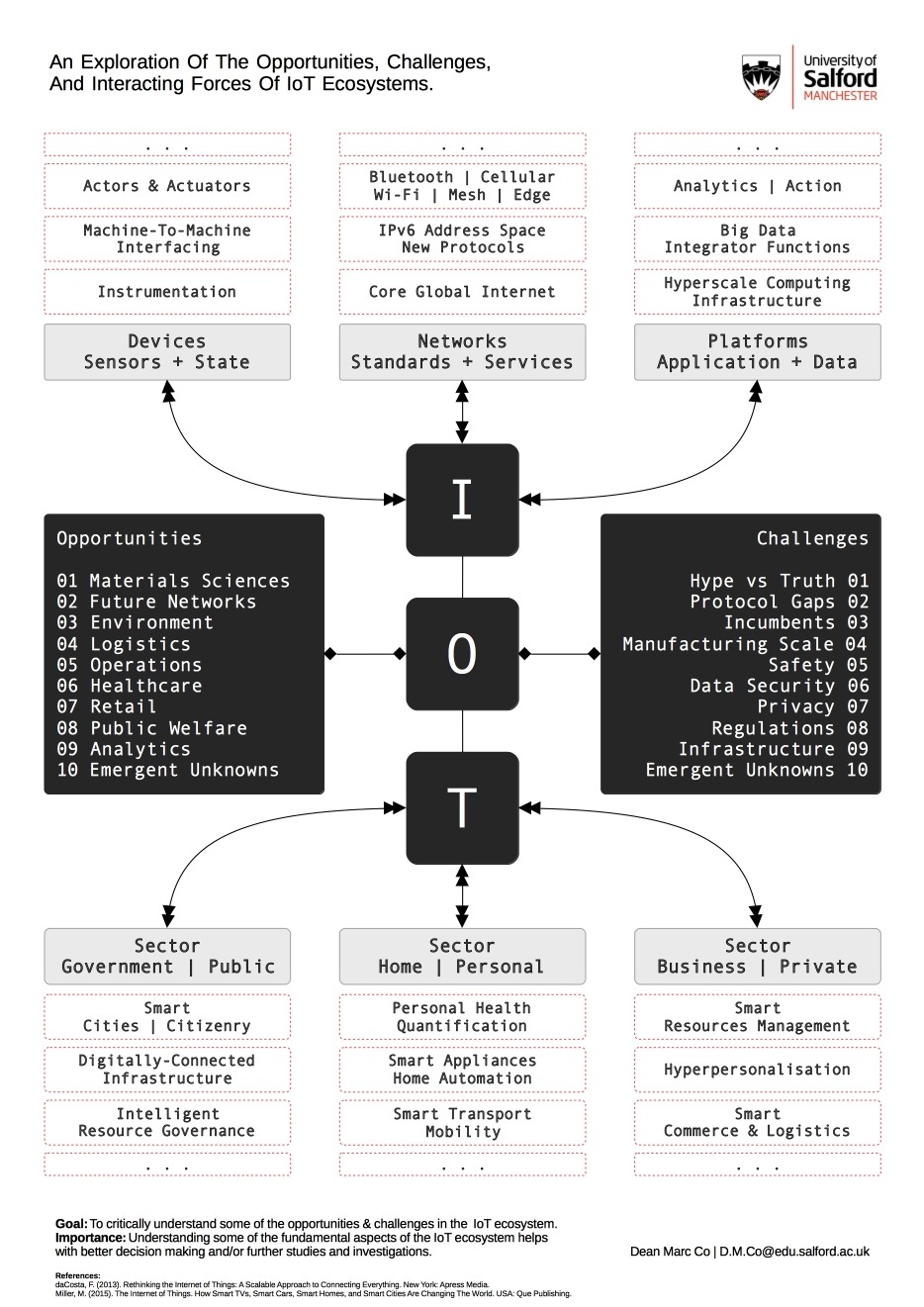
2. Key Components of IoT
IoT systems consist of several key components that work together to enable the exchange of data and communication between devices. These components include sensors and actuators, which gather and transmit information from the physical environment; connectivity options such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks; and IoT platforms that provide the infrastructure for data storage, processing, and application development.
In addition, edge computing plays a crucial role in IoT by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Security measures, including encryption and authentication protocols, are also essential components of IoT to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to connected devices and networks.
3. Applications of IoT in Smart Homes
IoT has revolutionized the concept of smart homes by enabling the interconnectivity of various devices and systems within a household. Smart home applications of IoT include home automation (e.g., smart lighting, thermostats, and security systems), energy management, and remote monitoring of appliances and utilities. IoT devices in smart homes can be controlled and monitored through smartphone apps or voice commands, providing convenience and energy efficiency for homeowners.
Moreover, IoT in smart homes contributes to enhanced safety and security through features such as smart locks, surveillance cameras, and smoke detectors that can send real-time alerts to homeowners’ mobile devices. The integration of IoT in smart homes continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for personalized and interconnected living spaces.
4. IoT in Healthcare and Wearable Devices
The integration of IoT technology in healthcare has led to the development of wearable devices that can monitor vital signs, track physical activity, and provide real-time health data to patients and healthcare providers. These wearable IoT devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, enable continuous health monitoring and early detection of medical conditions, promoting proactive healthcare management and personalized treatment plans.
Furthermore, IoT plays a crucial role in remote patient monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to monitor patients’ health status from a distance and intervene promptly when necessary. The use of IoT in healthcare has the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce hospital readmissions, and enhance the overall quality of care through data-driven insights and predictive analytics.
5. Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Smart Manufacturing
Industrial IoT (IIoT) refers to the application of IoT technology in industrial settings, including manufacturing plants, logistics operations, and supply chain management. IIoT enables the integration of sensors, machines, and production systems to create “smart factories” that can optimize production processes, improve operational efficiency, and enable predictive maintenance of equipment.
By leveraging real-time data from interconnected devices, IIoT empowers manufacturers to monitor equipment performance, identify production bottlenecks, and implement predictive quality control measures. The adoption of IIoT solutions can lead to reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and increased overall productivity in the industrial sector.
6. IoT and Environmental Monitoring
IoT technology has been instrumental in environmental monitoring and sustainability efforts by enabling the collection of real-time data on air and water quality, weather patterns, and ecological changes. IoT sensors and monitoring devices deployed in natural environments, urban areas, and industrial sites provide valuable insights for environmental conservation, disaster management, and climate research.
By analyzing the data collected through IoT-enabled environmental monitoring systems, policymakers, researchers, and environmental organizations can make informed decisions to address environmental challenges, mitigate pollution, and protect natural resources. The use of IoT in environmental monitoring contributes to a more proactive and data-driven approach to environmental stewardship.
7. IoT Security and Privacy Considerations
As the number of connected devices and IoT applications continues to grow, ensuring the security and privacy of IoT systems has become a critical concern. IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access, posing risks to personal privacy, financial security, and critical infrastructure.
To address these challenges, IoT security measures such as end-to-end encryption, secure authentication, and regular software updates are essential to protect IoT ecosystems from potential threats. Additionally, privacy regulations and industry standards play a crucial role in shaping the responsible deployment and use of IoT technology while safeguarding users’ privacy rights and data protection.
8. The Future of IoT: AI and Edge Computing
The future of IoT is closely intertwined with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and edge computing. AI-powered IoT systems can analyze large volumes of data generated by interconnected devices, enabling proactive decision-making, predictive maintenance, and autonomous operation of IoT ecosystems.
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized cloud servers, enhances the efficiency and responsiveness of IoT applications. By leveraging the synergy of AI and edge computing, the future of IoT holds promise for more intelligent, autonomous, and context-aware systems that can adapt to dynamic environments and user preferences.
9. IoT Standards and Interoperability
Establishing industry-wide standards and protocols for IoT devices and platforms is crucial to ensure interoperability, compatibility, and seamless integration of diverse IoT systems. IoT standards address communication protocols, data formats, and security requirements, enabling different IoT devices and applications to exchange data and operate cohesively.
Interoperability among IoT devices and platforms is essential for creating unified ecosystems that can support a wide range of applications and services, regardless of the manufacturer or technology provider. Industry consortia, standardization bodies, and regulatory initiatives play a key role in shaping IoT standards and promoting collaboration among stakeholders in the IoT ecosystem.
10. Ethical and Social Implications of IoT
The widespread adoption of IoT technology raises ethical and social considerations related to data privacy, consent, and the ethical use of IoT-generated data. As IoT devices collect and analyze vast amounts of personal and behavioral data, concerns about surveillance, data ownership, and algorithmic biases have emerged, prompting discussions on ethical frameworks and responsible IoT deployment.
Furthermore, the impact of IoT on employment, human interactions, and societal structures is a topic of ongoing debate, as automation and connectivity reshape traditional roles and practices. Addressing ethical and social implications of IoT requires a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates input from policymakers, ethicists, technologists, and community stakeholders to ensure that IoT development aligns with ethical principles and societal values.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a revolutionary concept that is shaping the way we interact with technology and the world around us. As we continue to explore the potential of IoT, it becomes increasingly clear that its applications are limitless. From smart homes and cities to healthcare and agriculture, IoT is transforming various industries and improving efficiency, productivity, and quality of life. By embracing IoT, individuals and businesses can benefit from increased connectivity, automation, and data-driven insights.
As we learn more about Exploring the Internet of Things (IoT), it becomes evident that the practical applications are endless. In our daily lives, IoT can be used to automate household tasks, monitor health and fitness, enhance security, and optimize energy usage. Businesses can leverage IoT to track inventory, improve logistics, analyze consumer behavior, and enhance customer experiences. By incorporating IoT into our lives, we can save time, reduce costs, and make more informed decisions.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are some examples of everyday IoT devices?
Some examples of everyday IoT devices include smart thermostats, fitness trackers, smart home assistants, connected cars, and wearable health monitors.
2. Is IoT technology secure?
IoT technology can pose security risks, but measures such as encryption, authentication, and regular software updates can help mitigate these risks.
3. How is IoT impacting the healthcare industry?
IoT is revolutionizing healthcare through remote patient monitoring, smart medical devices, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment plans.
Join the Conversation
We’d love to hear your thoughts on Exploring the Internet of Things (IoT). Have you implemented any IoT devices in your life? How do you see IoT shaping the future? Share your experiences and join the discussion below!
Leave a Reply